자바스크립트 문법 (7)
<자바스크립트 객체>
자바스크립트의 기본 타입은 객체(object)입니다.
객체란 이름(name)과 값(value)으로 구성된 프로퍼티의 정렬되지 않은 집합
var cat = "나비";
var kitty = { name:"나비", family:"코리안 숏 헤어", "age":1, weight:"1kg"};
document.write(cat + "<br>")
document.write(kitty.name);//나비
나비
var person = {
name: "홍길동",
birthday: "030219",
pld : "1234567",
fulld : function(){
return this.birthday + this.pld;
}
};
document.write(person.name + "<br>")
document.write(person["name"])<객체의 메소드 참조>
var person = {
name: "홍길동",
birthday: "030219",
pld : "1234567",
fulld : function(){
return this.birthday + this.pld;
}
};
document.write(person.fulld() + "<br>")
document.write(person.fulld)//0302191234567
function () { return this.birthday + this.pld; }
+) 메소드를 참조할때 이름 뒤에 괄호를 붙이지 않으면 메소드가 아닌 프로퍼티 그 자체를
참조하게 된다.

var obj = Object.create(null, {
x : {value:100, enumerable: true},
y : {value:200, enumerable: true}
});
document.write(obj.x);
document.write(obj.y);
document.write(Object.getPrototypeOf(obj))

Object.ptotype 객체는 어떠한 프로토타입도 가지지 않으며, 아무런 프로퍼티도 상속받지 않음
또한, JS에 내장된 모든 생성자나 사용자 정의 생성자는 바로 이 객체를 프로토타입으로 가짐
프로토타입의 생성
프로토타입을 생성하는 가장 기본적 방법 => 객체 생성자 함수를 작성하는 것
생성자 함수를 작성하고 new 연산자를 사용해 객체를 생성하면, 같은 프로토 타입을 가지는
객체들을 생성할 수 있음
function Dog(color,name,age) {
this.color = color;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
var myDog = new Dog("흰색","마루",1);
document.write("우리 집 강아지는 " + myDog.name + "라는 이름의 " + myDog.color + " 털이 매력적인 강아지입니다.");
객체에 프로퍼티 및 메소드 추가
이미 생성된 객체에 새로운 프로퍼티나 메소드를 추가하는 방법
function Dog(color,name,age) {
this.color = color;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
var myDog = new Dog("흰색","마루",1);
myDog.family = "시베리안 허스키";
myDog.breed = function() {
return this.color + " " + this.family
}
document.write("우리 집 강아지는 " + myDog.breed() + "입니다.");
//우리 집 강아지는 흰색 시베리안 허스키입니다.
위의 예제에서 새롭게 추가된 breed() 메소드는 오직 myDog 인스턴스에만 추가됨
이미 생성된 다른 Dog객체나 차후 생성되는 어떠한 다른 Dog객체에도 추가되지 않음.
프로토타입에 프로퍼티 및 메소드 추가
프로토타입에 새로운 프로퍼티나 메소드를 추가하는 것은 객체에 추가할 때와는 다른 방법을 사용해야 함
프로토타입의 경우에는 생성자 함수에 직접 추가해야만 이후에 생성되는 모든 다른 객체에도 적용할 수 있음
function Dog(color,name,age){
this.color = color;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.family = "시베리안 허스키"
this.breed = function() {
return this.color + " " + this.family;
};
}
var myDog = new Dog("흰색","마루",1);
var otherDog = new Dog("갈색","콩이",3);
document.write("우리 집 강아지는 " + myDog.family + "이고, 친구네 집 강아지도 " + otherDog.family + "입니다.");//우리 집 강아지는 시베리안 허스키이고, 친구네 집 강아지도 시베리안 허스키입니다.
prototype 프로퍼티
prototype 프로퍼티를 이용하면 현재 존재하고 있는 프로토타입에 새로운 프로퍼티나 메소드를 손쉽게 추가할 수 있음
function Dog(color,name,age) {
this.color = color;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
Dog.prototype.family = "시베리안 허스키";
Dog.prototype.breed = function(){
return this.color + " " + this.family;
}
var myDog = new Dog("흰색", "마루", 1);
var hisDog = new Dog("갈색", "콩이", 3);
document.write("우리 집 강아지는 " + myDog.family + "이고, 친구네 집 강아지도 " + hisDog.family + "입니다.");
document.write("우리 집 강아지의 품종은 " + myDog.breed() + "입니다.<br>");
document.write("친구네 집 강아지의 품종은 " + hisDog.breed() + "입니다.");객체 다루기

function Dog(color,name,age){
this.color = color;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
var myDog = new Dog("흰색","마루",1);
Object.defineProperty(myDog, 'color', {enumerable:false});
document.write(Object.keys(myDog) + "<br>");
document.write(Object.getOwnPropertyNames(myDog));//name,age
color,name,age
객체간의 비교
function Dog(color, name, age) {
this.color = color;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
var myDog = new Dog("흰색", "마루", 1);
var hisDog = new Dog("흰색", "마루", 1);
document.write((myDog == hisDog) + "<br>"); // false
document.write((myDog === hisDog) + "<br>"); // false
var herDog = hisDog;
document.write((hisDog == herDog) + "<br>"); // true
document.write((hisDog === herDog) + "<br>"); // truemyDog와 hisDog는 별개의 객체이므로 동등 연산자와 일치 연산자를 비교했을 때 false
herDog에 hisDog 객체를 대입(객체 레퍼런스) 하게되면 변수 herDog는 hisDog 객체를 가리키게됨
즉, 객체 레퍼런스는 객체 자체를 저장하는 것이 아니라, 객체가 위치한 주소를 저장하는 것
따라서 모두 true를 반환하게 됨
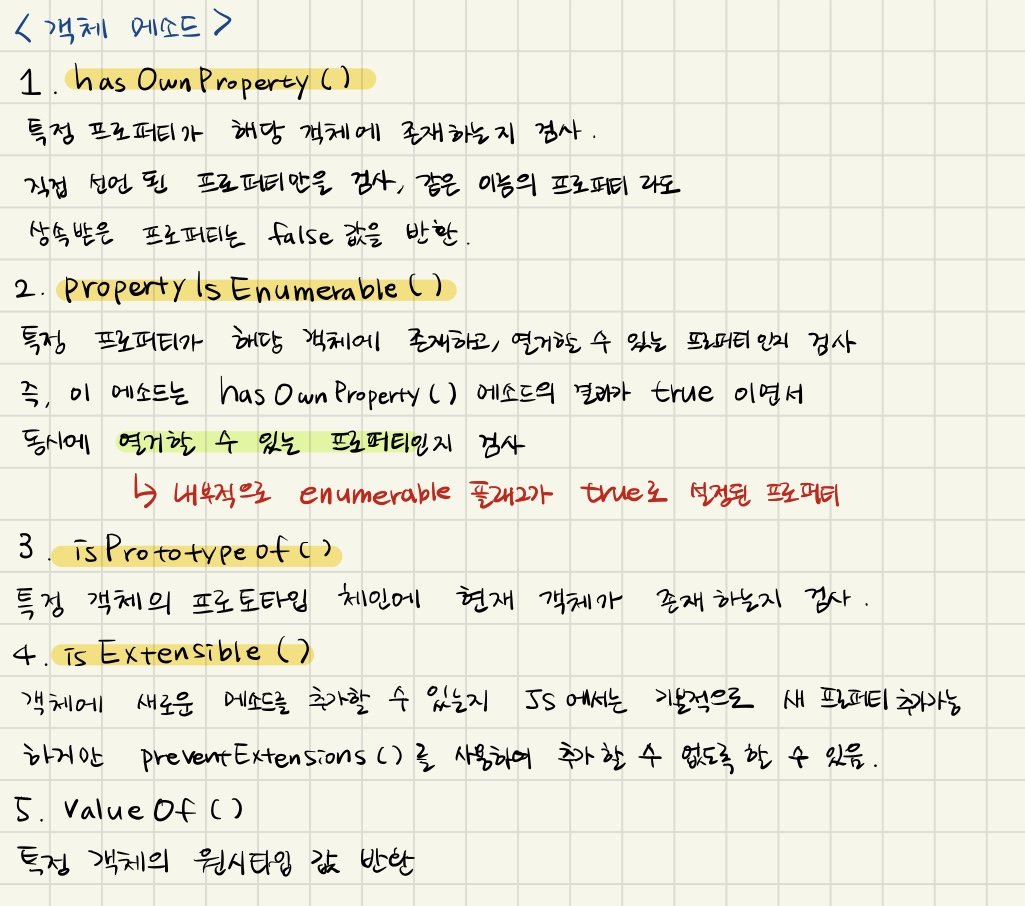
객체 프로퍼티와 메소드
function func(n) {
this.number = n;
}
myFunc = new func(4);
document.write(myFunc + 5); //1
func.prototype.valueOf = function(){
return this.number;
}
document.write(myFunc + 5) //2
1.객체의 valueOf() 메소드를 정의하지 않았으므로 [object Object]5 가 출력
2.prototype프로퍼티를 이용하여valueOf() 메소드를 정의, 따라서 number 프로퍼티 값 반환, 정상적으로 산술 연산 수행 9 출력
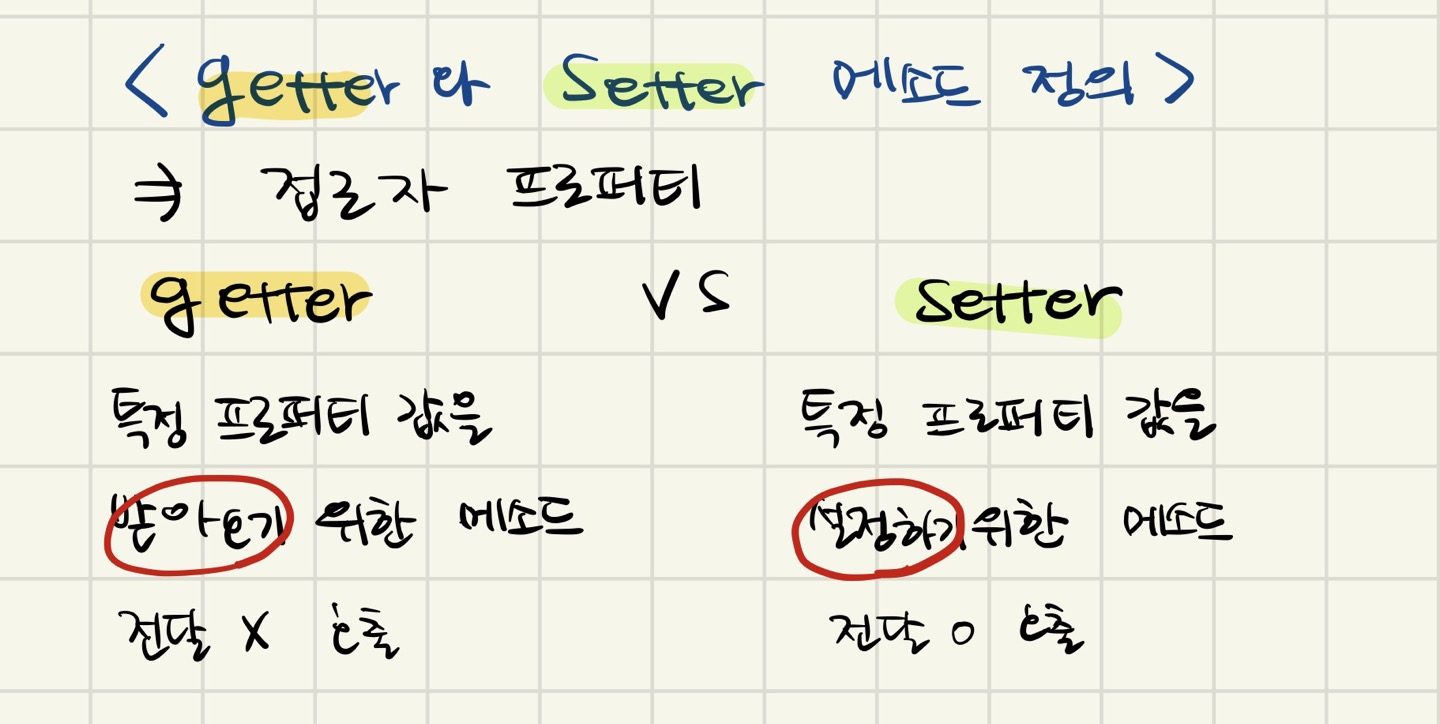
getter
var gildong = {age : 18};
document.write(gildong.age + "<br>");
Object.defineProperty(gildong, "americanAge", {get:function(){
return this.age-1
}})
document.write(gildong.americanAge);
gildong 객체에 americanAge라는 프로퍼티를 추가할 때 get 키워드를 사용하여 getter 메소드 정의
따라서 해당 프로퍼티를 참조하려고 할 때는 내부적으로 미리 정의한 getter 메소드가 자동으로 호출
setter
var gildong = {age:18};
gildong.age = 20;
document.write(gildong.age + "<br>");
Object.defineProperty(gildong, "changeAge", {set:function(n){
this.age = this.age -n
}});
gildong.changeAge = 5;
document.write(gildong.age);